You probably realize your car has a catalytic converter, but beyond that, you may not understand how this amazing little device works. The technology was designed by a French mechanical engineer in the 1950s and first introduced to the public in the 1970s. It wasn’t until American emission control standards began to tighten up in the early 1980s that they became standard issue on vehicles sold in the United States.
What It Does
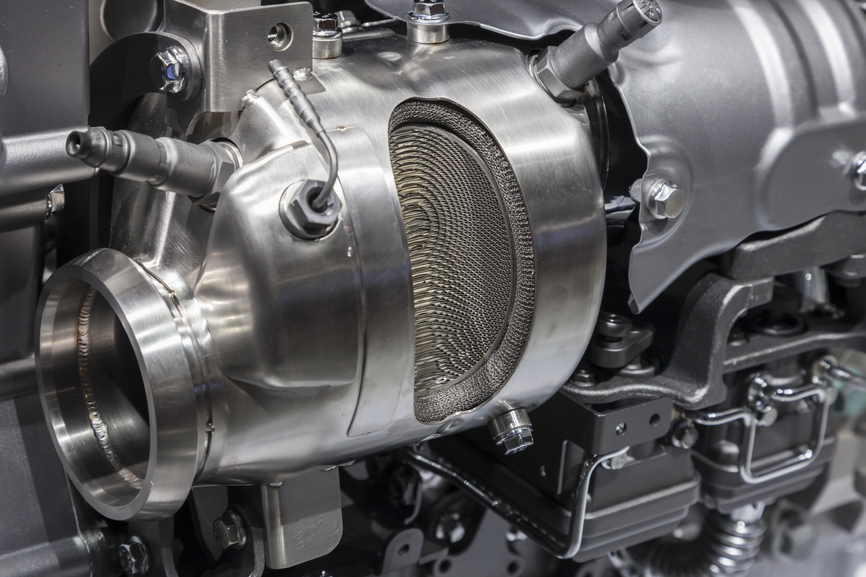
A critical component of your car’s emission control system, the catalytic converter transforms harmful compounds exhausted through the engine’s combustion process into harmless gases. Shaped a bit like a muffler itself, it is typically located in the undercarriage of the vehicle near the front seats. It connects the engine with the muffler and, in a brilliant but simple feat of engineering, converts dangerous emissions as they pass through en route to the tailpipe. Early models restricted exhaust flow, which was terrible for gas mileage and performance and even posed some danger of causing a fire underneath the car. Today’s versions have overcome these problems, and special high-flow versions are available for high-performance cars.
How It Works
If you’ve heard that a catalytic converter is worth its weight in gold, that’s not far off. The center core is composed of ceramic pathways that are coated with precious metals in a honeycomb configuration. Rhodium, platinum and palladium are the primary catalysts, although iron, magnesium, nickel and cerium are also used. As the exhaust passes through, the catalysts reduce and oxygenate it, transforming it almost instantaneously into its inert final form and sending it on to the muffler.
What It Filters
Originally, auto manufacturers outfitted vehicles that ran on leaded gasoline with catalytic equipment. Some components in leaded fuel were prone to clogging it, however, destroying its functions and requiring replacement. This led, at least in part, to the widespread adoption of unleaded gas in the United States. The converter works on three main exhaust compounds. The first one, hydrocarbons, are contained in unburned gasoline put forth in vehicle exhaust. The next compound, carbon monoxide, is produced as the result of the combustion process. The final compound filtered is nitrogen oxides, created by the engine’s high level of generated heat, which is the product responsible for acid rain. The process turns highly poisonous carbon monoxide to harmless carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water. Nitrogen oxides are converted into their base components of nitrogen and oxygen.
Emission Time in Sandy and Salt Lake understands how important your entire emissions system is, not only for the continued operation of your vehicle, but also for controlling pollution. Offering on-the-spot vehicle registration renewals, they are the locally owned and operated experts that can also help keep your car running right, catalytic converter and all.
